We offer a number of low impact Energy Solutions to support energy reduction and which can be fully funded, part-funded or Capex free and which are available for Micro Business, SME and Industrial & Commercial clients. Contact us today to find out how we can support your business in reducing energy usage and costs.
SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SOLUTIONS

Solar Photovoltaic (PV) panels allow you to generate your own electricity using energy from the sun. They don't need direct sunlight only daylight, so they also work on cloudy days. Investing in solar panels and revolutionises the carbon footprint, profitability and branding credentials of businesses.
PV cells are made from layers of semi-conducting material, usually silicon. When light shines on the cell it creates an electric field across the layers. The stronger the sunshine, the more electricity is produced. Groups of cells are mounted together in panels or modules that can either be mounted on your roof or on the ground. The power of a PV cell is measured in kilowatts peak (kWp).
That's the rate at which it generates energy at peak performance in full direct sunlight during the summer. PV cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Most PV systems are made up of panels that fit on top of an existing roof, but you can also fit solar tiles.
Benefits at a glance
Significantly reduce business overheads, improve business operations and increase your bottom line with savings on daytime electricity costs.
•Reduce on-site grid energy used and reliance on the National Grid
•Reduce your carbon footprint: increase sustainability credentials & improve your reputation
•Law and Legislation: offset the cost of energy audits under the ESOS scheme
Investing in solar PV can still deliver a ROI of up to 24% as well as provide a range of further benefits.
By generating your own electricity you could save on your energy bills. Plus with the Government’s Feed-in Tariff, you could be paid for every kilowatt hour (kWh) you generate.
LED LIGHTING SOLUTIONS

LED is a highly energy efficient lighting technology, and has the potential to fundamentally change the future of lighting. LED lighting is very different from other lighting sources such as incandescent bulbs and compact fluorescent lamp (CFLs). Key differences include the following:
Light Source: LEDs are the size of a fleck of pepper, and a mix of red, green, and blue LEDs is typically used to make white light.
Direction: LEDs emit light in a specific direction, reducing the need for reflectors and diffusers that can trap light. This feature makes LEDs more efficient for many uses such as recessed downlights and task lighting. With other types of lighting, the light must be reflected to the desired direction and more than half of the light may never leave the fixture.
Heat: LEDs emit very little heat. In comparison, incandescent bulbs release 90% of their energy as heat and CFLs release about 80% of their energy as heat.
The high efficiency and directional nature of LEDs makes them ideal for many industrial uses. LEDs are increasingly common in street lights, parking garage lighting, walkway and other outdoor area lighting, refrigerated case lighting, modular lighting, and task lighting.
Why LED?
• virtually zero maintenance
• long operating life span - up to 10 years
• better quality and clarity of light
• eco friendly - no toxic chemicals
• reduces carbon footprint
HEAT PUMP SOLUTIONS
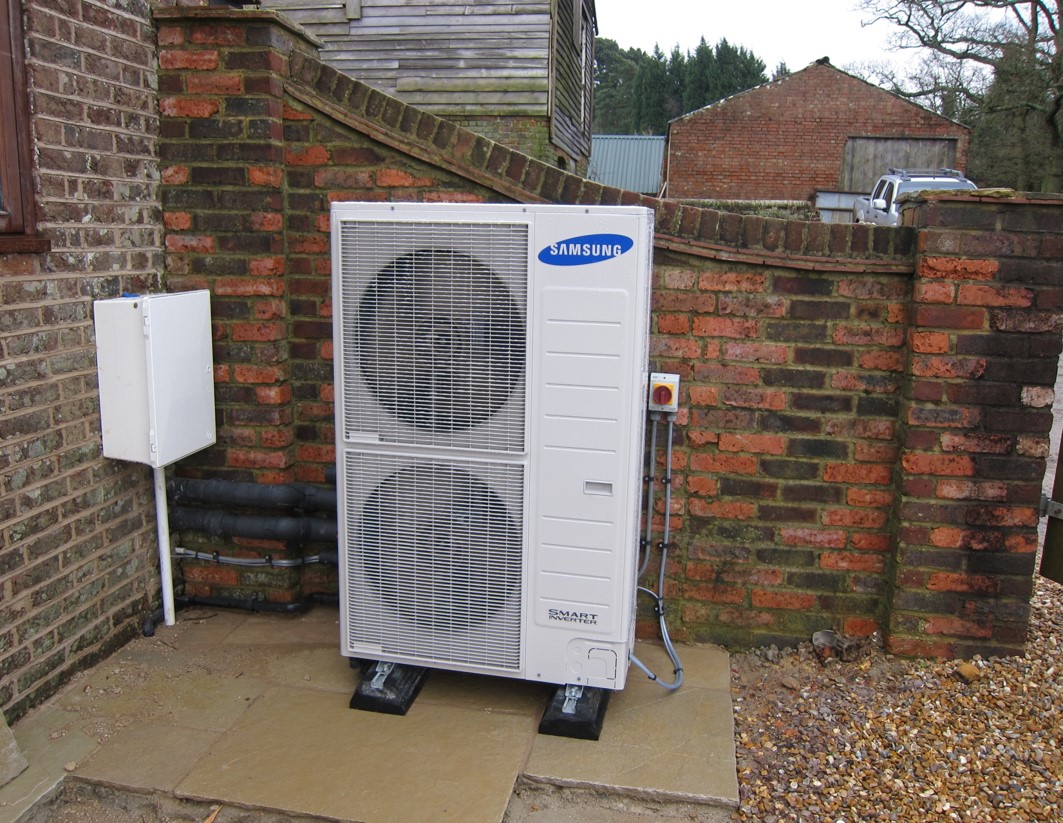

Heat pumps run on electricity, though the heat it utilises is renewable. A high coefficient of performance or COP is one of the most prominent advantages of air source heat pumps. It accounts for 300-400%, meaning that for one unit of power it consumes, it generates up to 4 units of renewable energy.
Heat pumps function much like an ordinary refrigerator in your kitchen that gets heat from the inside. An air source heat pump acts in a reversed way - it extracts heat from the outside ambient air and uses it for indoor heating. Its external unit looks similar to the air conditioner.
Ground source heat pump
A ground source heat pump can be used to extract heat energy from the ground in winter and to transfer the heat into buildings. Equally it can be used to provide a very efficient mechanism for heat to escape from buildings down into the ground in summer.
Ground source heat pumps are suitable for a wide variety of buildings and are particularly appropriate for low environmental impact projects.
They can be installed anywhere in the UK, using a borehole or shallow trenches or, less commonly, by extracting heat from a pond, a lake or the sea. Heat collecting pipes in a closed loop, containing water (with a little antifreeze) are used to extract this stored energy, which can then be used to provide space heating and domestic hot water.
Heat pumps can also be reversed in summer to provide cooling. GSHPs are cheaper to run than oil boilers and can be cheaper than running gas boilers.
Ground source heat pumps are very well suited to commercial buildings, especially those which have a need for cooling in summer as well as heating in winter.
BIOMASS BOILER SOLUTIONS
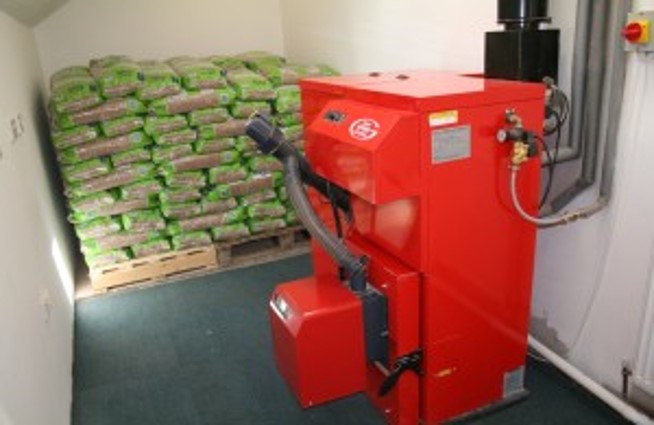

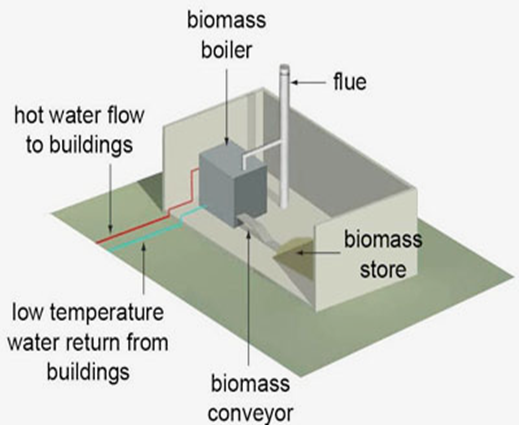
Biomass boilers work by burning wood pellets, logs or animal waste to provide central heating and hot water. Switching from traditional gas heating can help your business save up to 50% on fuel costs and 100% on carbon emissions.
In some instances we can provide a biomass boiler free of charge, however should you choose to fund the purchase and installation yourself you would be eligible to receive Commercial Renewable Heat Incentive payments as a guaranteed income for up to 20 years.
A biomass boiler works by burning wood fuel such as wood pellets, wood chip or logs to create heat.
On a biomass boiler there is a storage area (hopper) where the wood fuel is kept and then the actual boiler where the fuel is ignited. The wood fuel is automatically fed into the boiler from the hopper and then ignited by an auto start. The temperature is controlled via an electronic thermostat.
COMMERCIAL BATTERY STORAGE
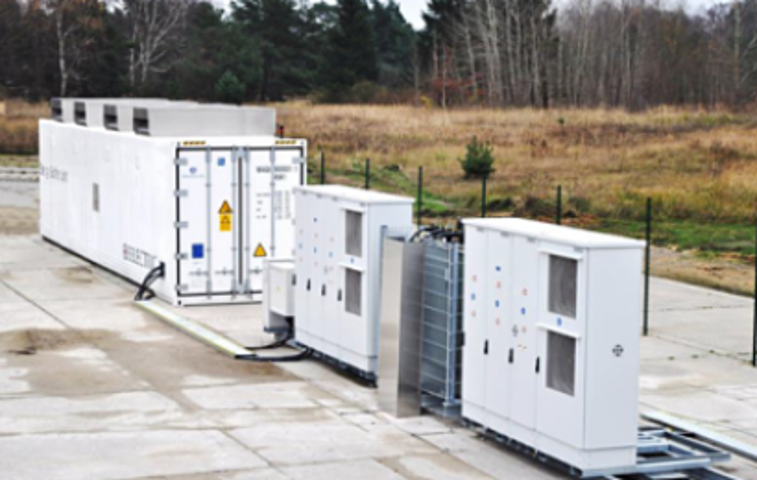

Today, modern electricity systems are evolving towards a generation mix that is more reliant on wind and solar to meet environmental targets.
While renewable energy sources support these targets they also tend to be decentralised, less predictable and less flexible, while some are not available (solar PV) to meet the winter peak demand. This increases the requirement for demand side balancing services, known as Demand Side Response (DSR). These services help the system operator, National Grid, to balance supply and demand at times of system stress, vital to maintaining the UK’s power supplies.
A feasibility study would be conducted using your half hourly data and would then be presented to yourselves showing cost returns and benefits.
How battery storage or Energy Storage System (ESS) generates revenue.
The ESS will identify when it is commercially attractive to charge/discharge. This includes limiting the discharge, as to avoid exporting to the grid, whilst maintaining the batteries high level of efficiency.
Furthermore, since some losses are present when both charging and discharging, the model will avoid over charging/discharging past the state of charge required to maintain the grid constraints imposed.
Triad Management
Every year the Transmission System Operators (TSO) can recover a maximum revenue for the maintenance of the system from its network users. This is known as the Transmission Use of Network Service (TNUoS) and is comprised of ‘forward looking’ charges and residual charges to ensure the total revenue is recovered.
The Triad charging structure is part of the ‘forward looking’ TNUoS charge and is levied by taking a user’s average power usage across the three half hours of highest demand on the transmission system (triad periods). The triad periods are measured between November and February whilst remaining at least 10 days apart. With a triad warning system in place, a user can reliably reduce their usage and thus their TNUoS charge. The current average triad charge rate is £45/kW.
ELECTRIC VEHICLE CHARGING POINTS

An electric vehicle charging station, also called EV charging station, electric recharging point, charging point, is an element in an infrastructure that supplies electric energy for the recharging of electric vehicles, such as plug-in electric vehicles, including electric cars and plug-in hybrids.
As plug-in hybrid electric vehicles and battery electric vehicle ownership are expanding, there is a growing need for widely distributed publicly accessible charging stations.
EV charge points are primarily defined by the power (in kW) they can produce and therefore at what speed they are capable of charging an EV.
There are three main EV charging speeds. Rapid charging units (43, 50, or 120kW) can provide an 80% charge in around 30 minutes; Fast charging points (7-22kW) can fully recharge some models in 3-4 hours; Slow charging points (up to 3kW) are used for longer charging times, around 6-8 hours.
BOREHOLE WATER WELL
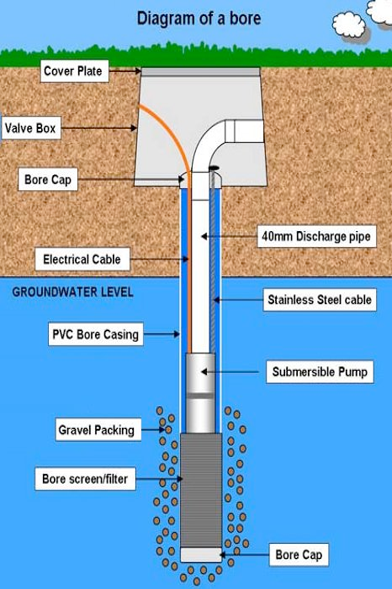
You can greatly reduce water costs by installing your own water access via a borehole water well.
You can extract 20 000 litres, 4400 gallons of water from the well daily at no charge or licence requirements. A water well is a borehole drilled in the ground to access water in underground aquifers.
Drilled wells are typically cased with a factory-made pipe, typically steel or plastic. The casing is constructed by welding, either chemically or thermodynamically, segments of casing together.
The water is drawn via an electric submersible pump into storage tanks Wells can vary greatly in depth, water volume and water quality.
MONITORING EQUIPMENT

We can easily install monitoring systems which will give clients in depth analytics on their utility supplies.
The systems monitor in real time, the utility usage, C02 emissions and wasted electric, gas and water. This will help them understand when their services are efficient and where they can be adapted to become more economical without affecting their productivity.
This information can then be mapped as a benchmark for forthcoming years, to improve energy efficiency and to predict seasonal changes in their consumption.
Power factor correction and Voltage Optimisation
Power factor correction is the evaluation of your energy supply to interpret how efficiently your electricity is being utilised. By measuring your inflows of energy against your "useful output" we can establish how much electricity is being wasted and amend this ratio.
What Effect Does Power Factor Correction Have On Motor Rating and Efficiency ?
All motors have a rating for efficiency in the form of power factor with the ultimate power factor described as 1.00pf, although most motors will operate well below the ultimate efficiency level and consume more energy.
The combined effect of a number of motors will normally result in a poor power factor and low efficiency, it is not uncommon for a manufacturer to operate with a power factor as poor as 0.70pf or 70% efficiency resulting in higher energy bills.
Power Factor Correction addresses this inefficiency and delivers real measurable energy savings by reducing power consumption, removing reactive power charges on electricity bills and reducing demand and carbon emissions.





